Spring Batch AWS Series (II): Remote Chunking
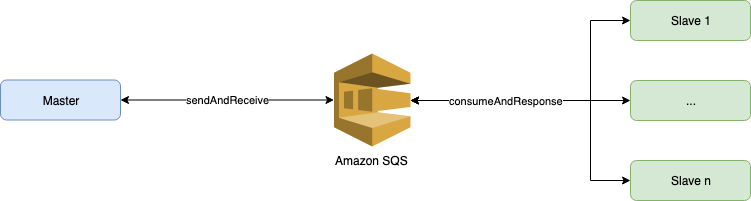
In this post we are going to implement the first step of our Spring Batch AWS Series using Remote Chunking. This step will send a chunk of numbers and the slaves will log the numbers that are prime.
Description
In Remote Chunking the Step processing is split across multiple processes, in our case communicating with each other using AWS SQS. This pattern is useful when the Master is not a bottleneck
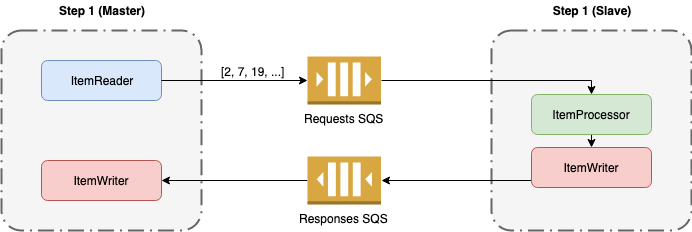
With Remote Chunking the data is read by the master and sent to the slaves using SQS for processing. Once the process finishes, the result of the slaves will be returned to the master.
Masterdoes all the I/O operationsSlavedoesn’t need database access to get the information. This arrives through SQS messages.
Common configuration
We need to configure next tools:
- Localstack: It’s used for simulate AWS SQS queues in local.
- Postgresql: It’s used for store Spring Batch metadata about jobs and steps.
The next docker-compose.yml contains all the necesary for our projects:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
version: '3'
services:
postgres:
image: postgres:9.6.8-alpine
restart: always
ports:
- 5432:5432
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: user
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password
POSTGRES_DB: db
localstack:
image: localstack/localstack
ports:
- "4567-4583:4567-4583"
environment:
- SERVICES=sqs
- DATA_DIR=${DATA_DIR- }
- PORT_WEB_UI=${PORT_WEB_UI- }
- LAMBDA_EXECUTOR=${LAMBDA_EXECUTOR- }
- DOCKER_HOST=unix:///var/run/docker.sock
volumes:
- "${TMPDIR:-/tmp/localstack}:/tmp/localstack"
- "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"
Master project
This section shows the most important aspect of our master application, how to comunicate the requests and responses with the slave.
“Master => Slave” Integration Flow (Request outbounds)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow step1RequestIntegrationFlow() {
return IntegrationFlows
.from(step1RequestMesssageChannel())
.transform(chunkRequestToJsonTransformer)
.handle(sqsMessageHandler())
.get();
}
- Read from
step1RequestMessageChannelchannel. We have to define a special writer (ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter) that will write to thestep1RequestMessageChannel. - The previous channel will receive a
ChunkRequestobject with all the necessary information for the slaves. In this step we’ll transform this object in Json using our own tranformChunkRequestToJsonTransformer. - Send to SQS. This handler will send the previous message to SQS using
SqsMessageHandler
“Slave => Master” Integration Flow (Response inbounds)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow step1ResponseIntegrationFlow() {
return IntegrationFlows
.from(sqsMessageDrivenChannelAdapter())
.transform(jsonToChunkResponseTransformer)
.channel(step1ResponseMessageChannel()).get();
}
- Read from SQS messages using
SqsMessageDrivenChannelAdapterand send the json to the transformer. - Transform the received json in
ChunkResponseusingJsonToChunkResponseTransformer - Send the
ChunkResponsetostep1ResponseMessageChannelthat is configured inChunkMessageChannelItemWriteras reply channel. Now Spring will mark the step with the result received.
Slave project
This section shows the communication with the master.
“Master => Slave” Integration Flow (Request inbounds)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow step1RequestIntegrationFlow() {
return IntegrationFlows
.from(buildRequestSqsMessageDrivenChannelAdapter())
.transform(jsonToChunkRequestTransformer)
.handle(step1ChunkProcessorChunkHandler())
.channel(step1ResponseMessageChannel())
.get();
}
- Read from SQS messages using
SqsMessageDrivenChannelAdapterand send the json to the transformer. - Transform the received json in
ChunkRequestusingJsonToChunkRequestTranformer - Send the
ChunkRequesttostep1ChunkProcessorChunkHandler()that is a special handler where you could define your processor and/or writter. - The result will be sent to
step1ResponseMessageChannel
“Slave => Master” Integration Flow (Response outbounds)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow step1ResponseIntegrationFlow() {
return IntegrationFlows
.from(step1ResponseMessageChannel())
.transform(chunkResponseToJsonTransformer)
.handle(sqsMessageHandler())
.get();
}
- Read from
step1ResponseMessageChanneland send the receivedChunkResponseto the transformer. - Transform the object in json using
ChunkResponseToJsonTransformer - Send the previous message to response queue in SQS.
How to run
- Run the docker-compose.yml file
docker-compose upTMPDIR=/private$TMPDIR docker-compose up(MAC users)
-
Create the queues if don’t exists
1 2 3 4
aws sqs create-queue --endpoint http://localhost:4576 --queue-name step1-request.fifo --attributes '{"FifoQueue": "true", "ContentBasedDeduplication":"true"}' aws sqs create-queue --endpoint http://localhost:4576 --queue-name step1-response.fifo --attributes '{"FifoQueue": "true", "ContentBasedDeduplication":"true"}' -
Run one or more slaves using the main class
com.frandorado.springbatchawsintegrationslave.SpringBatchAwsIntegrationSlaveApplication - Run the master using the main application
com.frandorado.springbatchawsintegrationmaster.SpringBatchAwsIntegrationMasterApplication
References
[1] Link to the project in Github
 Never miss a story from us, subscribe to our newsletter
Never miss a story from us, subscribe to our newsletter